Triathlon and Genetics Tests
This article is rare to find on the internet. I presented this seminar few years ago when the athletic genetics tests had become trendy. I collected a lot of information from articles and genetics specialists about these tests. Here you can read the summary about genetics and relation with triathlon.
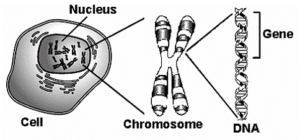
Inside the nucleus are chromosomes which are made of DNA. This is the code to make you you.
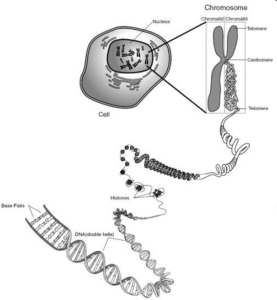
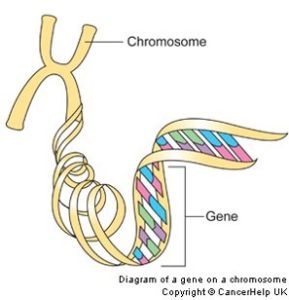
One section of DNA is a gene.
Chromosomes are the carriers of the gene.
Chromosome are not visible in active nucleus but are clearly seen during cell division.
As example, here are some genes notable for their function:
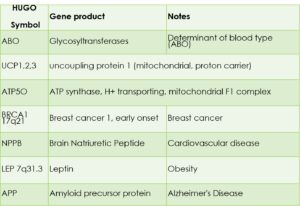
ACTN3
Alpha-actinin-3,
F-actin protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN3 gene.
Alpha-actinin is an actin-binding protein with multiple roles in different cell types. This gene expression is limited to skeletal muscle. It is localized to the Z-disc and analogous dense bodies, where it helps to anchor the myofibrillar actin filaments.
There are two types of muscle fibers:
- slow twitch (type I)
- and fast twitch (type II).
There are two types of filaments:
- actin (thin filaments)
- and myosin (thick filaments)
Actin filaments are stabilized by actin binding proteins known as actinins of which there are two main types, type 2 and type 3.
Each of these is encoded by a specific gene, ACTN2 and ACTN3 respectively.
ACTN2 is expressed in all skeletal muscle fibers
whereas
ACTN3 is expressed only in fast twitch fibers.
The RS1815739 mutation (R577X)
has been identified in the ACTN3 gene
studies in elite athletes have shown that the ACTN3 gene may influence athletic performance.
While the non-mutant version of the gene is associated with sprint performance,
the mutant version is associated with endurance.
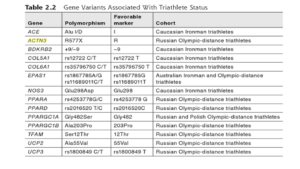
ACE gene (Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme)
This gene encodes enzyme Angiotensin II is a potent vasopressor and aldosterone-stimulating peptide that controls blood pressure and fluid-electrolyte balance.
COL5A1 gene (Collagen, Type V, Alpha 1)
The COL5A1 gene provides instructions for making a component of collagen. Collagens form a family of proteins that strengthen and support many tissues in the body, including skin, ligaments, bones, tendons, muscles
BDKRB2 Gene (Bradykinin Receptor B2)
This gene encodes a receptor for bradykinin. The 9 aa bradykinin peptide elicits many responses including smooth muscle spasm and pain fiber stimulation. This receptor associates with G proteins that stimulate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system.
COL6A1 (Collagen, Type VI, Alpha )
The COL6A1 gene provides instructions for making one component of type VI collagen, which is a flexible protein that surrounds muscle cells.
EPAS1 (Endothelial PAS Domain Protein 1)
The EPAS1 gene, often known as HIF2A, provides instructions for making a protein called hypoxia-inducible factor 2-alpha (HIF-2α). This protein is one part (subunit) of a larger protein complex called HIF, which plays a critical role in the body’s ability to adapt to changing oxygen levels.
NOS3 GENE (Nitric Oxide Synthase 3 )
Nitric oxide is a reactive free radical which acts as a biologic mediator in several processes, including neurotransmission and antimicrobial and antitumoral activities. Nitric oxide is synthesized from L-arginine by nitric oxide synthases.
PPARA GENE (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Nuclear )
Peroxisomes are subcellular organelles found in plants and animals that contain enzymes for respiration and for cholesterol and lipid metabolism.
PPARD (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta)
PPARs play essential roles in the regulation of cellular differentiation, development, and metabolism (carbohydrate, lipid,protein)
PPARGC1A (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma, Coactivator 1)
The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional coactivator that regulates the genes involved in energy metabolism.
It provides a direct link between external physiological stimuli and the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis, and is a major factor that regulates muscle fiber type determination. This protein may be also involved in controlling blood pressure, regulating cellular cholesterol homoeostasis, and the development of obesity.
PPARGC1B gene
The protein encoded by this gene stimulates the activity of estrogen receptor alpha, nuclear respiratory factor 1, and glucocorticoid receptor. The encoded protein may be involved in fat oxidation, non-oxidative glucose metabolism, and the regulation of energy expenditure.
TFAM gene (Transcription Factor A, Mitochondrial)
This gene encodes a key mitochondrial transcription factor containing two high mobility group motifs. The encoded protein also functions in mitochondrial DNA replication and repair.
UCP2 and UCP3 (Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2, 3 )
Are members of the larger family of mitochondrial anion carrier proteins and UCPs separate oxidative phosphorylation from ATP synthesis

Have questions about this?
Comment below and I’ll answer them!
I’m always checking on my new blog for new comments…
So if you need help solving your training problems, feel free to comment and I’ll pop back on and answer them as soon as possible!
Comment below now!

